Sleep and Adoption
/"People who say they sleep like a baby usually don't have one." - Leo J. Burke
The Problem ...
Dr. Sears: "Thou shalt cosleep, unless you don't really want that special bond we like to call attachment."
Dr. Ferber: "Thou shalt let them cry, unless you don't really want that thing we like to call a good night's sleep."
Dr. Dobson: "Good night's sleep? Have you considered a good night's spanking?"
Dr. Weissbluth: "If you don't sleep train them now, there's a 92% chance they'll be huffing paint behind the Quik-E-Mart by age 16."
That neighbor whose kid would have slept well even if raised by wolves: "Really? Our precious Tyler slept through the night since he was 2 months old ..."
Attachment therapist: "Never let their feet touch the ground ..."
Movement therapist: "But if she doesn't learn to crawl soon, her left brain will never talk to her right brain!"
Mother-in-law: "You're spoiling that child - she needs to cry it out."
APmom on your 4am chat group: "Cherish these magical middle-of-the-night bonding opportunities - not ever sleeping is a glorious gift!"
Dad: "Honey, the baby's crying ..."
Mom: "Honey, why don't you go cherish this particular magical moment ..."
Too many experts, not enough left brains talking to right brains. Too much opinion, not enough research. Too much crying, not enough sleeping. What's an adoptive parent to do? Read on, my sleepless friend, as we tiptoe through the too-often tendentious topic of SLEEP.
What is this thing you call sleep?
So much depends on adequate, restful sleep. We've got important work to do at night, from physical growth (80% of growth hormone is secreted while we sleep), to mental growth (integrating themes and memories of the day), to recharging cellular batteries, and other functions that we just haven't understood yet.
We all sleep in cycles, but children have unique sleep patterns. As infants, they have many sleep periods through a day, and a greater proportion of active (REM) sleep - about 50%, with the other half being "quiet sleep", a precursor to more developed Stages 1-4 of non-REM sleep. By 3-4 months, melatonin turns on, and infants organize their sleep into more of a day/night pattern. This is why it's silly to expect children to sleep through the night before 4 months.
By 6 months, the full cycle of non-REM and REM sleep is happening, but infants can get into Stages 3 and 4 (deep sleep) much faster than adults, and still spend more time in REM sleep. Deep non-REM sleep is important, since it's the most restorative phase of sleep, and is also when growth hormone is released. REM sleep seems to process and organize new memories and events, and is crucial to mental wellbeing.
By 3-4 years of age, children's sleep finally resembles adult sleep in quality, with 4-6 sleep cycles. The first half of the night has more non-REM sleep, with more REM sleep in the second half.
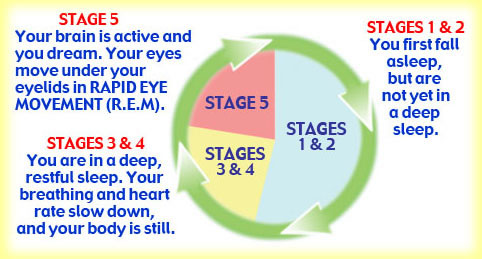
Image from SleepForKids.org, an excellent resource from the National Sleep Foundation
You'd think with something this important we'd be born good at it ... but we're not. Not even close. Just like walking and talking, the ability to fall asleep and stay asleep is something that is learned at developmentally appropriate times. How and when to help your child learn is the hard part.
Why bother? Sleep deprivation is being increasingly linked to emotional and behavioral problems, poor concentration, impulsivity, ADHD misdiagnoses, impaired learning, reduced physical performance, poor growth, headaches and bellyaches, and decreased immune function, not to mention family stress.
Sleeping through the night?
As for "sleeping through the night" ... nobody does. We all wake up to some degree several times a night, often when our sleep cycles from deep to lighter sleep. Arousals after REM sleep also occur, and tend to leave you more awake and alert. You may not be up long enough to remember it (that takes 3-5 minutes), but you do wake up, even without the "help" of your less sleep-skilled child. Our goal, thus, is not to "sleep through the night", but to promote healthy sleep associations and self-soothing skills so that your kids will fall back asleep when they wake 5 times every night.
How common are night wakings that you'll notice? By 4-6 months, babies are physiologically capable of sleeping through without feeding, but according to the 2004 Sleep in America poll, 70% of these infants still wake up and need help or attention, with 47% of toddlers, 36% of preschoolers, and 14% of school-age children also with notable wakenings. The numbers seem considerably higher in new adoptees, for reasons we'll address below. As far as other sleep difficulties go, the same poll revealed that 69% of all children experience one or more sleep problems, including stalling, bedtime resistance, and daytime sleepiness.
How much sleep does my child need?
The following table is based on sleep surveys and recommendations from the National Sleep Foundation:
While each child is unique, it's rare for kids to need much less sleep than these recommendations. However, there does seem to be individual variation in amount of needed sleep, as well as "night owl" vs "early bird" variation; these patterns are present from early childhood and are fairly stable. As for the naps, children who nap are happier, have better attention spans, may learn better, and arrive at bedtime without being overly tired. Good naps lead to good night-time sleep, and vice-versa. "Sleep begets sleep." Just try to keep naps from lasting into the later afternoon. For a great discussion of the how and why of naps for one and all, see Sleepless in America.
Special Concerns in New Adoptees
Sleep disturbances are far and away the biggest initial concern for the new adoptive families that come to our clinic. Most new international adoptees sleep well enough on the trip home - quite possibly because they're thoroughly overwhelmed and emotionally exhausted by this transition. When you arrive home, 1-2 days of jet lag per time zone crossed is typical, but children often recover before grownups.
Learning as much as possible about the prior sleep environment and bedtime routines can be very helpful. But since orphanages can have unnaturally long naps and early bedtimes (often aided by medication, sadly), you may not want to follow their timetable precisely. Remember that children from orphanages may never have been alone in a room, and will need a prolonged transition to sleeping by themselves. Children in foster care may have quite evolved bedtime routines, transitional objects, and sleep habits ... such as cosleeping, which is common in Korea and many other countries. Even the clothes they came in have reassuring smells and associations, so keep them around ...
If the "cry-it-out" methods work as advertised, then why do kids from orphanages who've unfortunately been crying-it-out their whole lives sleep so poorly at first? Well, since almost every aspect of bedtime and your child's new sleep environment is different and thus "wrong" at first, it's natural that new adoptees have difficulty falling asleep and falling back asleep during night arousals. Your child's grief at the loss of familiar caregivers may erupt at night, and when you come to console them they may be expecting someone else.
New adoptees are usually so overstimulated (we call it "Disneyland syndrome") that they may blow right through sleepytime into an adrenaline-addled second or third wind. Also, your child is experiencing dramatically more love and stimulation, is having rapid catchup development, and we know that children working on new skills often obsessively practice or at least cogitate upon these new milestones. Nightime is no exception, and it's not unusual to find children happily or unhappily attempting new feats in the crib.
Children experiencing parental love and attention for the first time are understandably reluctant to give it up because someone says it's "bedtime". The early stages of a new attachment have an insecure, "velcro" quality, so it's normal for new adoptees to be anxious and insecure around bedtime. If they won't even let you have a bathroom break, how are they suppose to handle the big kahuna of daily separations - bedtime in their own crib? Add to that the fact that it's developmentally normal for kids to have a flareup of separation anxiety at around 18 months, and you got quite an anxious child on your hands.
Plus ... it's scary in the dark, even for many "home-grown" kids. On top of that, think of all the negative associations with nighttime your adoptive child may have had. Being cold, soaked through the rags that served as diapers, in a hard metal crib, with no one answering your cries, and waking up to a different shift of caregivers is not a good memory. Neither is hearing your first parents yell and hurt each other late at night.
Finally, children with histories of prematurity, prenatal substance exposures, lack of early responsive, regulating caregiving, and stressful/traumatic experiences can literally be wired differently, with real neurologic differences in sensory processing and self-regulation. Children with oversensitivities to sound, light, or touch are more likely have difficulty filtering these inputs out at night. Children with poor emotional and self-regulation experience their emotions more intensely, and have difficulty self-soothing. The process of "attunement" (a powerful emotional connection in which the caregiver recognizes, connects with, and shares the child’s inner states) with a responsive caregiver is necessary to help your child identify, organize, and work through their emotions. That attunement, more than "crying-it-out", is what will rewire your child so that they develop genuine self-soothing skills. Try to see initial nightime wakenings with empathy for where they're coming from and what they're now experiencing.
For all of these reasons, most adoption professionals do not recommend sleep training that involves prolonged crying in the first few months home. You may have brought home an 18-month-old, but he/she may be emotionally younger in many ways, and your relationship itself is a bouncing brand new baby ... one that will keep you up more than you might like in the first few months. Plan on being more emotionally and physically available at night, and try to think of these nightime interactions as an opportunity for bonding, and a way to repeatedly show your new arrival that she is loved, safe, and well-cared for.
But keep your eyes on the prize - restful restorative sleep for all. It's never too early to set up good sleep habits, and help build self-soothing skills. You'll probably want to have both a transitional sleeping plan, and a longterm plan. Get the The No-Cry Sleep Solution for Toddlers and Preschoolers or Sleepless in America, and one of the "sleep training" books (Sleeping Through the Night is my favorite, but see our list of recommended Sleep Books), and get down to learning and soul-searching about what's going to work for your family in the short and long-term. Pantley's questionnaires can help guide the discussion, and the National Sleep Foundation's Children's Sleep Diary (pdf) can help analyze a school-age child's sleep patterns (or use this simpler sleep log for younger kids) ...
While the transitional plan should probably involve some parental presence during sleep onset and night arousals, the longterm plan is up to you. It's a emotionally loaded powder-keg of competing sleep philosophies out there, and I'm not going to light the fuse. If you are loving, attentive, and attuned during the day, and have been responsive to transitional sleep issues in the first months home, you do have my permission to move into some modified "gentle" sleep training if that's what you need to do (prolonged hysterical crying does feel traumatizing to many of us, though). You also have my blessing to cosleep 'til the cows come home, as long as you're all cosleeping and not cosleepless.
Bottom line - know thyself, and know thy children. If they have histories of trauma or neglect, you don't want to reinforce those stress-forged neuro-endocrine pathways by retraumatizing them. If a method feels like torture, or just isn't helping your child, then try something else. Sleep training is not a one-size-fits-all solution; some children may settle quickly after a brief fuss that blows off some of the stresses of the day. Some will cry for HOURS and devolve into a sweaty, snot-smeared, how-dare-you-do-this-to-me, too-frantic-to-sleep zombie. And they'll do this every time the routine gets off and you have to "re-sleep-train". Weigh the risks and benefits for your family. What's worse, lonely frantic crying and loss of loving, attuned care at night, or having a dangerously sleep-deprived, depressed, not-so-attuned parent during the day? There's no right answer to that ... you need to trust your instincts here. That said, I do think Mary Sheedy Kurcinka's Sleepless in America is the closest I've read to "the right answer", since she skillfully walks you down the path of what underlies your child's sleep issues, and helps you adjust your approach to your child's temperament. Very very highly recommended.
Let's get practical ...
After all this sleep theory, I know that you wanna get practical, so let's get into practical:
Zeitgebers
But first, more theory. Ha. Just kidding. Zeitgebers are the "time-givers", the environmental cues that set or reset our biological clocks. Because we run on a 25-hour clock, and the world runs on a 24-hour clock, we need daily cues to continually set our circadian rhythms. And trust me, you need these right now, especially if you just got off the plane.
- Light is the major zeitgeber - keep things dim in the hour before bedtime, dark at night except for a dim nightlight if necessary, and brightly lit through the day. A sunny breakfast first thing in the morning is ideal.
- Physical handling and eye contact are potent stimuli that can boost adrenaline levels. Keep the physical play and long intense gazes for daytime ... but soothing contact like rocking and gentle backrubs work well at night.
- Food routines can help maintain circadian rhythms, so try for consistency in your meal/snack/bottle schedule.
- Vigorous physical activity during the afternoon can make a big difference at night as well. Go for a big hike or playground session - your new arrival may have more energy than you think.
Bedtime Routines
Even if you're a free spontaneous spirit, your child is gonna need a bedtime routine. Young children thrive on predicability and routine, and that goes double for post-institutionalized children. How long should it be? How about 30-40 minutes ... sound too long? Well, how long does your child take to actually fall asleep after you "put them to bed"? Either you've just found some time that could be better spent on a cozy, bonding bedtime ritual, or you've won the sleep jackpot (don't tell the other parents). When things are going well is when it makes sense to trim it back to 20 minutes or so. Here are some ideas for your bedtime routine ...
- The whole hour before bedtime should be free of TV, computer games, vigorous play, or other stimulating activities.
- Sleepy-time snacks. Preempt the "I'm still huuuungry" calls with a healthy and even sleep-inducing bedtime snack. Complex carbohydrates, as well as turkey, peanut butter, bananas, soy and dairy products (which all contain tryptophan) can help you get your sleep on. Best eaten half an hour before bed.
- Review a pictorial sleep routine story that you wrote/drew together to reinforce the prebed ritual, and to confidently anticipate sleep successes. These sorts of personalized picture stories can really help in any anxious situation.
- Baths. Who doesn't love a bath? Well, the kids who got stuck under a cold faucet during diaper changes don't love the bath so much at first, but usually quickly warm up to the concept. Try not to make it a wet 'n wild play session, though. Remember - "you're getting sleeeeepy ..."
- Brush the teeth. Battery-powered toothbrushes are fun. So are tasty toothpastes. "Should I brush your teeth ... or your bellybutton?" Riff on your routine with absurd suggestions - they like it, and it builds language in the younger child or new English speaker. My niece likes to "teach the cat how to brush".
- Change into PJs ... and don't forget to change out of PJs in the morning - helps them be a more powerful sleep association.
- Bedtime bottle? The dentists just can't seem to win on this one ... but certainly no caloric beverages in the crib/bed, and it's nice to finish feeding 15 minutes before sleep to let saliva wash out some of those sugars, and to avoid setting up drinking as a sleep association that won't be there in the night. Milk, formula, and breastmilk are all soporrrific!
- Take a tour of the room, saying goodnight to all the favorite toys. Doubles as a language lesson for the English learners.
- A bedtime prayer is part of many bedtime rituals ... think about the content though. "If I die before I wake" might not be your best sleepytime thought.
- Put your child in his bed or crib and take up your station next to him. Oh look, was there a nice little not-too-stimulating surprise waiting in bed? Maybe a sticker? Or a new book? Isn't going to bed dandy?
- Do consider a gentle, soothing back massage or foot rub. Massage can work magic at bedtime, unless your child is overly sensitive to touch or ticklish ...
- Bookreading. Let your child choose 2-3 books. The lights should be really dim by now, so it's not about the pictures, it's about your soothing voice. If your voice needs a rest, try a tape of you reading, or an audiobook.
- "Goodnight, you princes of Maine, you Kings of New England ..." What will you leave your child with each night?
Bedtime Itself
It's earlier than you think. In fact the ideal toddler bedtime is often somewhere between 6:30 to 8pm.
- Use your sleep logs to keep track of when your child shows signs of sleepyness, and when he actually falls asleep.
- If you miss it, poof goes the easy sleepy bedtime - tired cranky adrenaline-addled children don't fall asleep well.
- If you get home from work late, you may need to rejigger that or make early mornings your quality time.
- If you're having sleep issues, you're well advised to keep sleep schedules the same 7 days a week. Which means keeping the bedtimes the same, but also not letting them sleep in much past their usual/appropriate wakeup time (ouch).
- That said, sometimes your child's current circadian rhythms has him going to bed later than you think. Try letting the bedtime start out later but inch it backwards by 10-15 minutes per night.
Falling Asleep
This here is the key, folks ... the associations your child has with that golden moment of falling asleep will be the ones she needs each time she wakes in the middle of the night. Do everything in your power to let that moment be on her own. No feeding, no rocking at that moment, if you can. Stay in the room at first, by all means, stay next to the bed or even in it if you must ... you can wean that later if you want. Falling asleep is hard to do if you are anxious and having difficulty letting go ... Here are some ideas to help with the weaning process, which may take weeks to months.
- Does your child have a "lovey", or transitional object, that can represent the emotional security she's building with you? If she didn't arrive with one, have an array of dolls, stuffed animals, and blankies around for a few days and see if she gravitates to one. Several of my patients swear by the Slumber Bear that plays womb sounds when jostled.
- When she settles on one, experienced parents keep backup loveys on hand, and even rotate them so they're equally worn and stinky.
- Maybe there are a few nonsense "errands" you need to do, in the room or out of it? But you'll be right back.
- In fact, you can set a silent timer like an hourglass egg timer or visual timer and tell her that you'll be back in 3 minutes when the timer is done. Come back, check on her briefly, and repeat. Make sure you do come back.
- Even if you're not doing the timer thing, coming back in for brief checkins when your child is not screaming for you is reassuring and rewards good bedtime behavior.
- Successes with independent falling asleep are often followed by fewer night wakings in 1-2 weeks.
Night Wakings
Remember the sleep study statistics - 70% of infants, 47% of toddlers, 36% of preschoolers, and 14% of school-age children wake and need help at least once per night - these are normal, folks.
- What's going on? Illness, teething, soaked diapers, recent stresses, new developmental milestones, night fears, night terrors, nightmares?
- Again, be more responsive at first than you might eventually plan to be ...
- But be as brief, boring, and minimalist in your interventions as possible.
- And give brief fussing a chance to subside on it's own - your child may be having one of those night arousals that doesn't involve fully waking up.
- Before you approach your wide-awake-and-screaming-at-4am child, take several slow, deep breaths, in through nose, out through mouth, focussing on a happier parenting moment or image of your child. Then go in.
- Keep the "deep cleansing breath/find your happiness" thing going while you're in there. Seriously - breathing and a calm, affectionate approach is SO helpful, day or night; HeartMath's "Quick Coherence technique" is one way to get there.
- Review your child's sleep associations - is there anything he falls asleep to that isn't there in the night?
- Is there something your child could do for himself that's self-soothing? Some of my older adoptees have cassette/CD players in bed with calming stories or music. If you played music at bedtime, can your child turn it back on easily?
- Pantley has several great suggestions - giving your older child one or two Get-Out-Of-Bed-Free cards, a "Sleep Fairy" that leaves stickers under the pillow when children have had a successful night (depending on what they're working on - reward incremental successes), and even wrapped prizes in the morning for kids that have a good quiet night.
- If you suspect night terrors, do less. They're more distressing for you than your child, and sleep experts discourage waking a child while they're having one. I've also heard that limiting fluids before bed may help, as full bladder might provoke night terrors.
Cozy Sleep Nooks
First things first - if there's a TV or computer in your child's room, banish it forthwith. They are the anti-sleep.
- Ideally the sleep area is for sleeping and quiet resting ONLY, and perhaps separated by curtains or other dividers from the rest of the room.
- Lots of stuffed friends can be reassuring, as are pictures of loved ones.
- Climb in and spend some time in it yourself. Is the mattress comfortable enough? Audible household or outdoor noises? Lights shining in from the hallway or street?
- Is there a place for you? Because that's the ultimate safe, secure "cozy sleep nook", at first. I think the ideal transitional solution is with one parent sacked out next to the child, since that will maintain a consistent sleep environment for the child when you eventually wean the parental presence.
- If you're not there during the night, something that explicitly reminds her of you is also very important - since smell is one of the most powerful shortcuts to our primitive brain, where our senses of anxiety and security come from, perhaps an aromatic worn t-shirt or pillowcase of yours? And some photographs of you together in a loving, calm moment can be reassuring in the night.
- Other options are having the crib or for an older child, a futon, next to your bed.
- Cosleeping is also a popular option at first. Some adoptive parents report that their child was easily weaned after a few months to their "big girl bed", but in general, once you start cosleeping it's the hardest to wean.
Light
- Seattle in the summer is brutal for sleep. Try creative window treatments like "blackout curtains", cardboard, aluminum foil (also adds a certain "blocking the alien mind control rays" touch to your decor) or whatever it takes to get that room dark.
- If you do use a nightlight, keep it as dim as possible to avoid vernichten das zeitgeber, ja? If you know what I mean ...
Sound
- White noise can be a godsend for sleep, and is one of the first things I recommend for light sleepers.
- A fan or aquarium pump running all night long can help drown out other intrusive noises.
- Ocean wave noise generators, womb noises, and heartbeat lullabies are other favorites.
Smell
- That lovey smells funky for a reason. Wash it at your peril.
- Something that smells like you can be soothing too. See above ...
- Aromatherapy - lavender and chamomile scents are felt to be relaxing as well. Try some "Badger Sleep Balm" ...
Touch
- Being wet in the night is trouble, so limit fluids in the 1-2 hours before bed, use diaper doublers, and consider a nice layer of protective diaper paste before bedtime.
- For children that seem to crave that snug-as-a-bug-in-a-rug sensation, often winding up wedged in the corner, perhaps a smallish sleeping bag or sleepsac would feel good. Grembo, LittleBigFoot, and others make zipup sleep bags for infants and toddlers. Tucking in the the sheets extra-tight may help at first, but they come undone; some parents have used a lycra sleeve around the mattress that the child slips into. Weighted blankets are available for older children with sensory issues as well.
- Many orphanage-raised children will have pronounced self-stim/self-soothing habits like rocking, head shaking or banging, ear fiddling, or sucking on lips or fingers. These do fade with time, but may still show up in time of stress.
Temperature
- The body tends to cool off at night, and people sleep better in a cooler environment.
- Warm baths followed by cool bedroom may help this process along.
Does my child have a sleep disorder?
Courtesy of Dr Mindell, the following list of sleep problems may indicate that your child has a sleep disorder. If these issues are present, if sleep issues are getting worse not better, or if you're at the end of your rope, please talk to your health care provider.
- Loud snoring, noisy breathing, or breathing pauses while sleeping
- Breathing through his mouth while sleeping
- Appearing confused or looking terrified when he awakens during the night
- Frequent sleepwalking
- Rocking to sleep or head banging when falling asleep or during the night (ed: actually very common in orphanage raised children, and thus only a problem for them if severe or persistent)
- Complaining of leg pains, "growing pains", or restless legs when trying to fall asleep at night
- Kicking his legs in a rhythmic fashion while sleeping
- Sleeping restlessly
- Frequent difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep
- Sleep difficulties leading to daytime behavior problems or irritability
Additional Sleep Resources
- Our favorite Sleep Books
- babysleep.com - most excellent advice and videos from pediatric sleep experts
- drcraigcanapari.com - my favorite online pediatric sleep doc (and college bestie)
Acknowledgements
Thanks to New Hope Child and Family Agency for the impetus, Elizabeth Pantley for many fab ideas, Drs. Mindell and Weissbluth for others, Dr. Greene for the zeitgebers, and our sleepless families for the inspiration.








